Photopharmacology, A New Generation Of Medicines
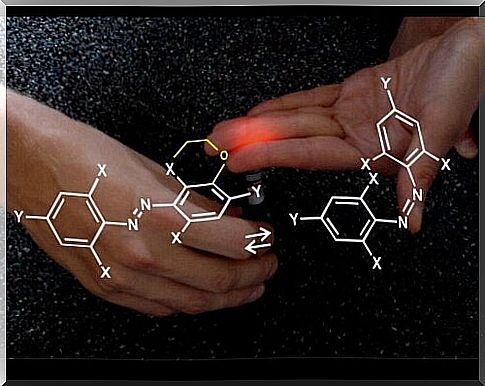
Photopharmacology is a new generation of medicines and is one of the most promising areas in pharmaceutical chemistry for the future. In general, there is a new generation of drugs that are activated by light. So they operate only on organs and tissues that need light and only when they are needed.
In addition, photopharmacology is able to minimize side effects. Science is very close to circulating the light-sensitive medicines that would make highly precise treatments a reality.
All indications are that these medications would be available for serious diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, diseases of the central nervous system and a long list that includes chronic pain and blindness. Therefore, photopharmacology is definitely a revolutionary alternative.
What is photopharmacology?
As we mentioned, there is a system that makes it possible to administer photosensitive medications. This means that they are only activated and take effect when combined with light. These properties mean that they have a high level of precision and only work at certain times and only in the area that requires it. This method is capable of affecting only one cell.
At the moment, the substances we ingest are working incorrectly in the body. A good example of this is first generation antihistamines. If a person is allergic and takes one of these drugs, the symptoms disappear. However, it is inevitable that they will develop drowsiness, since there are histamine receptors in the brain.
Although science has evolved a lot in the level of precision of drugs, it is still not possible to eliminate their side effects. With photopharmacology, this does not happen due to the selectivity of the site of action. This means that it only trades where it is supposed to trade.
Implantable microsystems
Implantable microsystems are one of the most interesting alternatives that scientists have proposed for directing and managing light-sensitive drugs in the body. They are small devices that doctors would put in the body and that would regulate the drug. They would place them where they are needed, when they are needed.
Bluetooth would control the implantable microsystems. This will allow them to go where they need to go, regulate the amount of light they need to deliver to activate the medicine, and control the exposure time and volume of the medicine.
So doctors could adjust the doses over time and even in real time. So they can perform a much more precise treatment and avoid side effects. This is important, especially when the medication is aggressive.

Cancer and heart applications
One of the areas where a likely application of photopharmacology is likely to take place is heart problems. For example, if you have an arrhythmia, one of these drugs may reduce your heart rate. It can also only exert its effect on the affected area, instead of affecting the whole heart.
Another of the most important applications of the new generation of drugs is the treatment of cancer. In addition, this technology allows a controlled release of the drug especially in the area where you have a tumor. In fact, there is a possibility that it will only attack malignant cells so that healthy cells do not have to suffer damage.
This new field, pharmacology, would make it possible to overcome the lack of selectivity of drugs. The result would be a treatment that is much more precise and free of side effects. Especially when it comes to cancer, this will mark a new era.
Conclusion
Today, researchers are studying other possible uses of this new generation of medications for health problems as serious as blindness, Alzheimer’s, diabetes and various types of infections. Doctors could treat virtually any disease with photopharmacology.
Regarding visual disturbances, Michael Telias, from the University of California at Berkeley, pointed out that blindness in animals has already been reversed with the application of this method. He indicated that they implanted light-sensitive molecules in the retina of some of them, and this allowed them to regain sight.
Researchers also believe that in the not too distant future they will have developed dressings with light-sensitive medicine to treat cancer. In addition, experts agree that this new pharmacology has wide areas to cover.