Anti-anxiety Medication: A Simple Guide

Anxiety is a natural behavior that people experience in response to any physical or psychological threat. However, it becomes a problem when this reaction is too excessive in relation to what triggers it. It can also result in a pathological state of anxiety that may require the use of anti-anxiety medications.
In addition, there is no clear boundary between normal anxiety and a pathological problem. But it can be said that it is at that point that your symptoms begin to interfere with your daily life.
Anxiety is a mental illness that is becoming more and more common around the world. For example, between 1990 and 2013, the number of people suffering from depression and anxiety increased from 416 to 615 million.
So, to understand why some medications are more appropriate than others, it is important to distinguish between the different types of anxiety:
- Some types of anxiety involve fear, such as panic attacks, social anxiety and phobia.
- Other anxiety is more general, without any clear cause or origin.
Treatment for anxiety with anti-anxiety medications
First, anxiolytic anti-anxiety medication relieves the symptoms of anxiety without having sedative effects or causing the patient to fall asleep. On the other hand, benzodiazepine is the ideal anti-anxiety medication because although it can cause sedation at higher doses, it can manage the anxiety effectively and at low risk for the patient.
However, this class of anti-anxiety drugs has the disadvantage that it produces known side effects, such as memory loss, addiction and high physical tolerance.
In addition, anti-anxiety medications must also be combined with a psychological approach to treatment. Also in the last decade, anti-anxiety medications and treatments have shifted from being based on traditional hypnotic or anti-anxiety medications to a wide range of drugs. And these drugs are used for other disorders of the central nervous system.
Benzodiazepines
The first benzodiazepine was chlordiazepoxide, synthesized in 1961. This class of drugs works by selectively binding to GABA receptors. In addition, this neurotransmitter mediates the inhibition of the central nervous system. Therefore, benzodiazepines facilitate the opening of chlorine-activated chlorine channels and highlight their inhibitory effects. They are also mildly sedative, relax the muscles and have anticonvulsant effects.
In addition, benzodiazepines are often used to treat acute anxiety. Initially, they have been effective against panic attacks and have even been used as enemas for epileptic children. They can be classified according to the time it takes for their effects to be felt:
- Short-acting benzodiazepines: midazolam, triazolam
- Intermediate: alprazolam, bromazepam, lorazepam, lormetazepam
- Long-acting: clobazam, chlorazepate, diazepam, chlordiazepoxide
In addition, the body easily absorbs these medications. However, anti-anxiety drugs can interact with psychotropic drugs, alcohol, barbiturates, opiates and antiallergic drugs. In addition, the dose for the elderly should be chosen carefully to avoid accumulation in the body.
The male side effects of these anti-anxiety drugs are:
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Amnesia
- Loss of coordination
In addition, all benzodiazepines may lead to higher tolerance (a gradual increase in the dose required to produce the same effect) and dependence. Therefore, it is recommended to gradually reduce the patient’s dose of benzodiazepines when attempting to stop treatment.
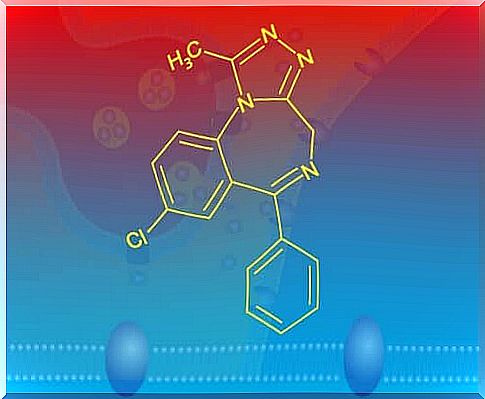
However, an acute overdose of benzodiazepines is significantly less dangerous than with other anti-anxiety drugs. However, it can lead to severe reduced breathing. In this situation, flumazenil is more typical. Doctors use it to reverse the same effects of alcohol poisoning.
Buspiron
Buspirone is an anti-anxiety drug among the class of serotonin 5-HT1a receptors. It can also help treat generalized anxiety disorder, but not phobias or social anxiety. And it does not have sedative, anticonvulsant or muscle relaxant effects. In addition, it has few drug interactions. The most important side effects are nausea, dizziness, headache and restlessness.
Anti-depressants for anxiety
These anti-anxiety medications are effective against generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety and phobias. Tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOH) also have several side effects, but can also be used.
In addition, in this class of medications, the following are often used to treat anxiety:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine or sertraline
- Serotonin reuptake inhibitors and norepinephrine, such as venlafaxine or duloxetine
Anti-epileptic drugs
In addition, anti-epileptic drugs such as gabapentin, pregabalin, valproate and levetiracetam are also effective in treating generalized anxiety disorder.
Atypical antipsychotics
Some types of atypical antipsychotics such as olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine and ziprasidone are effective in treating certain types of anxiety, including generalized anxiety disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
β-adrenergic antagonists
Finally, we would like to mention that propranolol is widely used to treat certain types of anxiety. It is especially useful for physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling and high heart rate.