What Is T-DM1 And What Is It Used For?
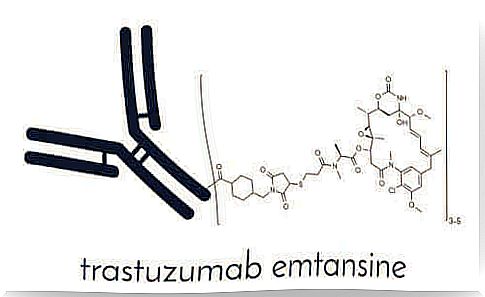
T-DM1 is a new, unique and selective antibody-drug conjugate approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer. HER2 is the protein “epidermal growth factor receptor 2” which favors the growth of cancer cells. You can find it on the market like Kadcyla.
T-DM1 consists of two compounds. The first is the well-known drug trastuzumab, which is an anti-HER2 antibody. The second component is a cytotoxic antimicrotubule molecule: DM1. Cytotoxic antimicrotubules refer to its ability to block the synthesis of microtubules in cell division, a mechanism we will discuss in more detail below.
The effect of T-DM1

18-20% of metastatic breast cancer cases are HER2-positive. In other words, they have an overexpression of the HER2 oncogene. Prior to the development of specific anti-HER2 therapies, the prognosis for patients with HER2-positive tumors was significantly worse than the rest.
An oncogene is a gene that, due to its ability to induce mutation or transformation, leads to the formation of cancer in a cell.
However, the development of trastuzumab, which was approved in 2000, counteracted the poor prognosis for HER2-positive breast cancer compared to HER2-negative. In 2014, another anti-HER2 drug was marketed: pertuzumab. The latest drug further prolongs overall survival in the first treatment of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer.
The second treatment for advanced HER2-positive breast cancer was the only one approved to date, and is a combination of cytotoxic drugs with capecitabine and lapatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of HER2 / EGFR.
A registry study called EMILIA compared treatment with T-DM1 versus treatment with lapatinib and capecitabine in patients with this type of breast cancer who had previously been treated with trastuzumab and a taxane.
The results of this study showed an increase in progression-free survival, an increase in overall survival and a profile of better tolerated side effects and a significant delay in symptoms until the progression of treatment with T-DM1.
How T-DM1 exerts its effect on the body
As we mentioned above, T-DM1 is the combination of two drugs: trastuzumab and DM1. T-DM1 combines the mechanisms of action of these two substances:
- Like trastuzumab, T-DM1 is able to bind HER2 and block the growth of tumor cells that overexpress this growth factor.
- It also presents the mechanism of action of DM1, which is why it can bind to tubulin.
As it inhibits tubulin, it prevents the cancer cells from dividing, which eventually causes cell death in apoptosis. The results of in vitro cytotoxicity analyzes show that DM1 is between 20 and 200 times more potent than vincataxanes and alkaloids.
The side effects of T-DM1
Side effects are the unwanted and unintended events that a patient can expect when starting treatment with a drug.
In this context, the most commonly reported side effects are nausea, tiredness and headache. ≥ 25% of patients suffered from them. Experts thus evaluated the safety of T-DM1 in a total of 1871 patients with breast cancer in various clinical studies. They found that the most common severe reactions were:
- Bleeding
- Dyspnoea
- Pain in bones and muscles
- Abdominal pain
- Thrombocytopenia
- And finally, vomiting.
Conclusion
The data reported from studies show that T-DM1 is a very important advance in the treatment of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer. It increases the survival of patients who have previously taken trastuzumab.
Despite these advances, HER2-positive cancer is still incurable. It is therefore necessary to find new, better tolerated and more effective treatments. We therefore have to continue researching breast cancer.